How Pond Delivers Reliable, Efficient and Resilient Power Solutions
 Author:
Author:
Kandi Howell | Program Director | kandi.howell@pondco.com
As the energy landscape continues to evolve, delivering power solutions that balance cost with resilience has become more crucial than ever. Pond offers comprehensive solutions for owners, operators, utilities, and end-users, encompassing everything from power generation to power delivery. Pond’s approach integrates advanced technologies and innovative infrastructure solutions to meet the unique challenges of modern power demands.
The Journey of Power Delivery
While electricity may seem readily available, it likely could have traveled hundreds of miles before it could be safely used. The journey begins at a power station, or power plant, where electricity is generated. Many plants still rely on traditional fuel sources, such as natural gas, coal, oil, or nuclear energy. However, renewable sources like hydroelectric, battery energy storage, solar, and wind power have become more integrated into the mix, with renewables making up more than 20% of power generation in the United States.
Once generated, high-voltage power lines transmit this electricity across the country. Along its route, the electricity will pass through electrical substations where transformers “step down” the voltage to safer, more usable levels. Lower-voltage distribution lines then carry this electricity to end-users, ensuring it arrives safely at homes, businesses, and other buildings.
Investing in Grid Resiliency
In 2022, the United States consumed approximately 4.07 trillion kWh of electricity — a record amount representing a more than 12% increase over the last 20 years. However, this rapid growth also creates challenges for grid reliability, particularly during peak energy seasons such as summer and winter. With the help of sophisticated models and advanced analytics, Pond supports utilities and grid operators to better predict and respond to demand fluctuations.
Some tools, such as load forecasting models, use historical data, weather patterns and economic indicators to identify usage patterns and predict peak demand. Other methods, like smart grid technology, use sensors and automated switching to anticipate and respond to demand. These tools are critical for keeping the grid online, but other threats persist, including weather-related outages, cyber-attacks, and failures in aging infrastructure. These threats underscore the importance of having resilient infrastructure that can better withstand disruptions, recover more rapidly and ensure continued power supply.
Investing in grid resilience is essential to keeping the power grid operating efficiently. By reducing vulnerabilities to power outages, blackouts, and malicious attacks, users can stay connected to the grid, even during outages and extreme weather events. Strengthening grid resilience enables utilities and operators to deliver reliable and continuous power to customers while supporting a more sustainable and adaptable energy future.
Modernizing the grid is also enhancing the safety of power delivery. More systems are being installed underground versus overhead where vegetation management may be difficult. Installing systems underground reduces electrical incidents, creates fewer outages from weather events, and produces a safer environment for consumers and workers.
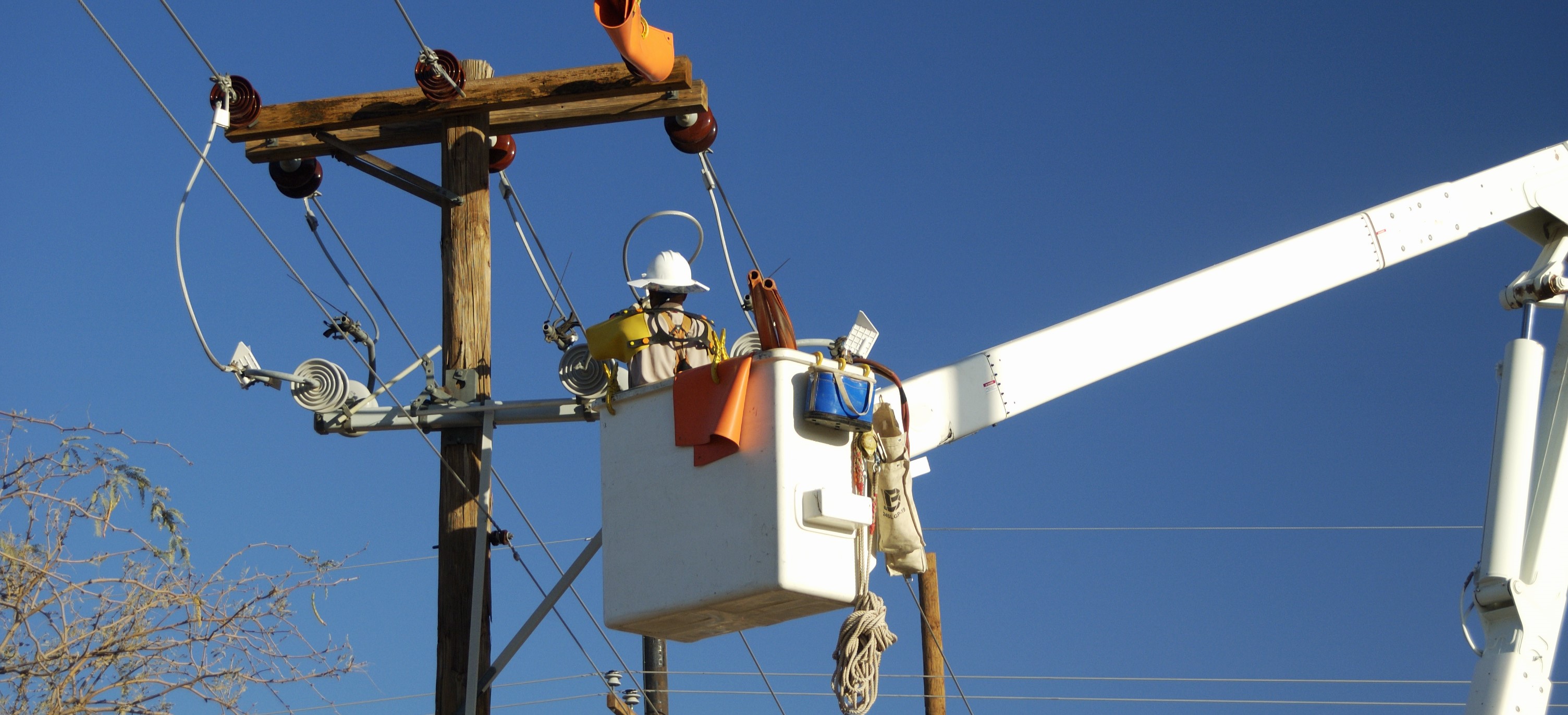

Future-proofing the Energy Grid
Much of the U.S. electrical infrastructure we see today dates back to the 1960s and 1970s when it was first installed. While the grid has undergone some upgrades, progress in integrating renewable energy has been slower. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 70% of transmission lines are over 25 years old and many are nearing the end of their 50- to 80-year lifespan.
This aging infrastructure poses additional risks to grid reliability and resiliency. These components are more prone to failures, outages, and vulnerabilities under stress from extreme weather events and shifting demand patterns. Upgrading these systems is essential not only to maintain consistent service, but also to support the integration of renewable energy sources. Plus, modernized infrastructure is required to manage renewables and measure the variability of wind, solar, and other sustainable power inputs.
Transitioning to a modernized grid requires retrofitting and replacing outdated infrastructure to enhance capacity and reliability. Technologies like smart grids, advanced metering systems, and energy storage solutions allow owners and operators to integrate newer technologies with minimal disruption. The United States has also experienced significant growth in zero-carbon energy sources like wind and solar power. Effective coordination amongst stakeholders is essential for successfully integrating these renewable sources into our grid and achieving a resilient and sustainable energy future.
Conclusion
Pond is dedicated to delivering resilient power solutions across the entire lifecycle of power delivery. By prioritizing reliability and sustainability, Pond helps clients navigate regulatory complexities, optimize energy efficiency, and achieve long-term cost savings, ensuring that power systems are not only effective today but future-ready for the challenges of tomorrow.
As demand increases and the need for future-ready power infrastructure grows, Pond's expertise supports the seamless integration of renewables and resilient energy solutions. Discover more about Pond's full-service Power Delivery program.